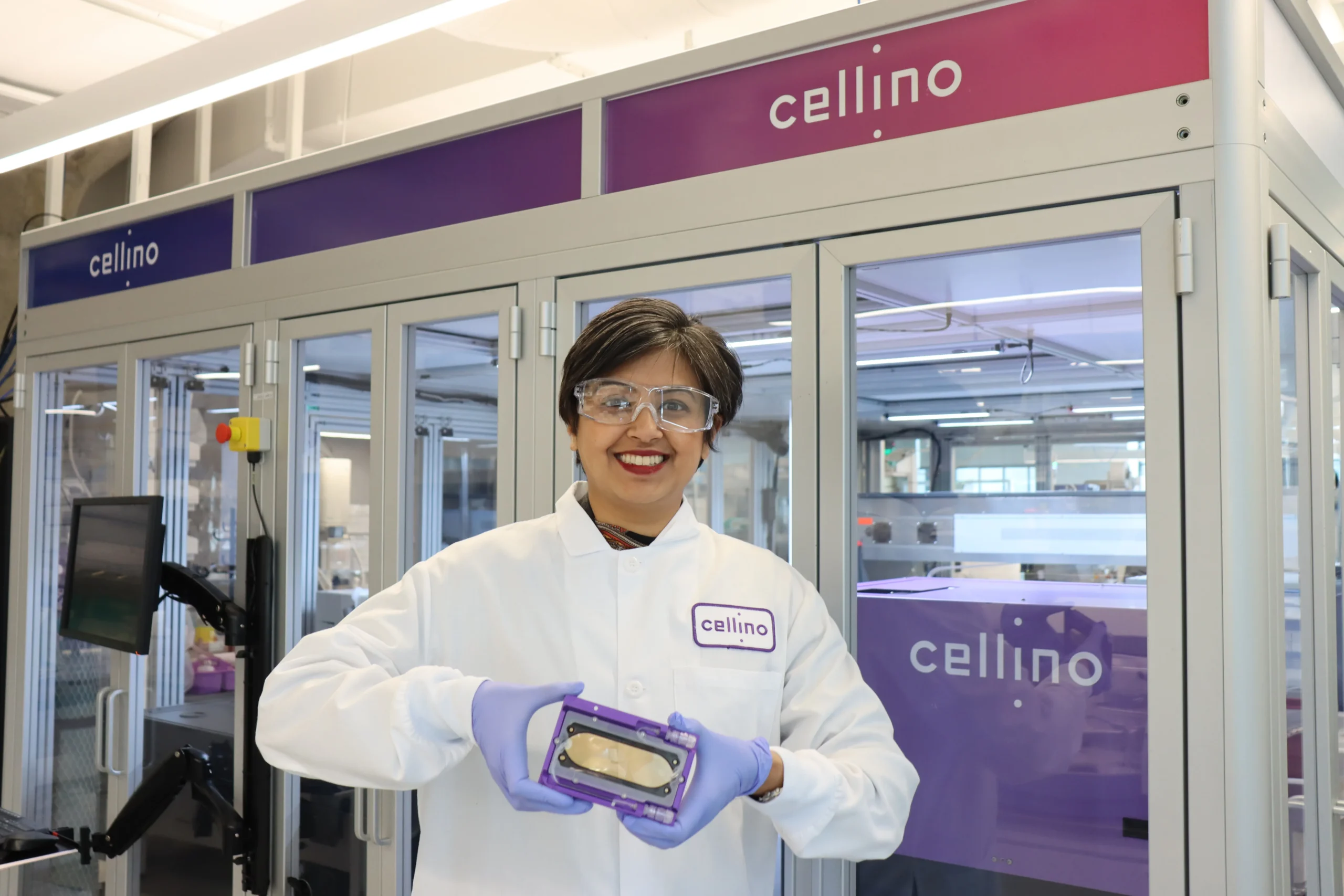
Cellino and Mass General Brigham GCTI Launch First Nebula-Powered iPSC Foundry for Scalable Autologous Biomanufacturing
A Landmark Collaboration in Regenerative Medicine
In a groundbreaking development for regenerative medicine, Cellino has announced its strategic collaboration with Mass General Brigham’s Gene and Cell Therapy Institute (GCTI) to establish the world’s first hospital-based autologous induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) Foundry. This initiative marks a significant leap in cell therapy, as it leverages cutting-edge artificial intelligence and biomanufacturing technologies to facilitate scalable, decentralized production of patient-specific stem cells and tissue therapies.
The Foundry will be powered by Cellino’s proprietary AI-driven Nebula platform, an advanced, autonomous biomanufacturing system designed to produce high-quality clinical-grade iPSCs with precision and scalability. This initiative is expected to revolutionize how cell and tissue therapies are developed and delivered, making personalized regenerative treatments more accessible to patients.
Massachusetts: A Hub for Biotech Innovation
Massachusetts has long been a leader in the biotech and life sciences industries, fostering collaborations that drive innovation and economic growth. Yvonne Hao, Massachusetts Economic Development Secretary and Board Co-Chair of the Massachusetts Life Sciences Center, highlighted the importance of this partnership in reinforcing the state’s role in cutting-edge biotechnology.

“Massachusetts remains the best state for unique partnerships to accelerate breakthroughs, create jobs, and change patients’ lives on a global scale,” said Hao. “We are so incredibly proud to have two leaders in industry and healthcare collaborate on next-generation biomanufacturing. Today’s announcement exemplifies the projects we must continue to champion in the next chapter of the Commonwealth’s Life Sciences Initiative.”
This initiative aligns with Massachusetts’ broader efforts to support life sciences innovation, attract top-tier talent, and create a sustainable ecosystem for biomanufacturing.
The iPSC Foundry: A Revolutionary Approach to Biomanufacturing
The newly launched iPSC Foundry is a fully integrated, on-site biomanufacturing facility based at Massachusetts General Hospital. The facility is designed to produce patient-specific iPSCs and derivative therapies while maintaining the highest standards of quality and efficiency.
At the core of the Foundry’s operations is the Nebula platform, a closed-cassette, autonomous biomanufacturing system that allows for precise and reproducible cell production. By deploying Nebula at the point of care, the Foundry minimizes contamination risks, reduces production timelines, and ensures the consistent manufacturing of personalized therapies.
A key advantage of Nebula is its ability to enable decentralized biomanufacturing—moving away from traditional centralized production models that are often costly and logistically challenging. By establishing autonomous production facilities within hospitals, this model aims to make cell and gene therapies more accessible and cost-effective, ultimately bringing personalized medicine closer to the patient.
“Centralized production of cell and gene therapies is not only expensive but also limits scalability,” explained Nathan Yozwiak, Head of Research at Mass General Brigham GCTI. “Decentralizing manufacturing through autonomous, on-site facilities may significantly cut costs and shorten the timeline from early clinical research to widespread commercial application.”
By implementing this decentralized approach, the iPSC Foundry sets the foundation for a nationwide network of hospital-based manufacturing hubs, a model that could redefine the future of regenerative medicine.
A Major Step in the Fight Against Parkinson’s Disease
One of the first major applications of the Foundry’s capabilities will be in developing an innovative Parkinson’s disease therapy. Using patient-specific iPSCs, the Foundry aims to create a breakthrough treatment that could provide long-term relief for millions of patients suffering from the debilitating neurodegenerative disorder.
Leading this effort is Dr. Jeffrey Schweitzer, a renowned neurosurgeon and the George A. Lopez, MD Endowed Chair in Neurosurgery at Mass General Brigham. Dr. Schweitzer is spearheading a Phase 1 clinical trial that seeks to evaluate the safety and efficacy of using a patient’s own cells for regenerative treatment.
“Using a patient’s own cells as a starting point has clear advantages, such as minimizing rejection risks, but making personalized cell therapy available to the millions who need it is a daunting task,” Dr. Schweitzer noted. “This collaboration represents a step toward reaching that goal.”
By leveraging the Foundry’s biomanufacturing capabilities, the trial aims to demonstrate how autologous cell therapies can be produced efficiently and at scale, potentially paving the way for broader clinical applications in neurodegenerative diseases and beyond.
The Transformational Impact of AI-Driven Biomanufacturing
Cellino’s collaboration with GCTI is not just about building a single facility—it represents a paradigm shift in how regenerative medicine is practiced. By integrating AI-driven automation into the biomanufacturing process, the Foundry enables rapid, cost-efficient production of personalized therapies.
“Our work with GCTI represents a major leap in making regenerative medicine more accessible and efficient,” said Nabiha Saklayen, Ph.D., CEO & Co-Founder of Cellino. “By integrating advanced AI-driven bioprocessing into hospital settings, we’re transforming traditional, centralized manufacturing into a faster, cost-effective, and patient-centric model.”
This transformation is particularly significant in the context of cell and gene therapy development, where manufacturing bottlenecks have historically been a major challenge. Traditional methods require extensive manual labor, highly specialized facilities, and complex logistics, leading to high costs and long production times. The Nebula-powered iPSC Foundry addresses these issues head-on, streamlining the entire manufacturing process from cell reprogramming to final therapeutic production.
By reducing costs, increasing efficiency, and enhancing quality control, this AI-driven approach has the potential to democratize access to cell therapies, making them viable treatment options for a broader patient population.
A Vision for the Future
The launch of the iPSC Foundry at Massachusetts General Hospital marks the beginning of a new era in biomanufacturing. With its decentralized, AI-powered model, this initiative could serve as a blueprint for future hospital-based biomanufacturing hubs across the country.
Looking ahead, Cellino and Mass General Brigham GCTI plan to expand the Foundry’s capabilities to support a wide range of regenerative medicine applications. Beyond Parkinson’s disease, the Foundry could play a crucial role in developing personalized treatments for conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, spinal cord injuries, and various forms of cancer.
As the field of regenerative medicine continues to evolve, the integration of AI-driven automation and decentralized manufacturing will be key to overcoming existing barriers and unlocking new possibilities for patient care. By pioneering this approach, Cellino and GCTI are not only advancing science but also transforming the way we think about medicine—bringing personalized, life-changing therapies to those who need them most.
With the establishment of the iPSC Foundry, the future of regenerative medicine has never been more promising.